순열(nPr)과 조합(nCr)을 헷갈리지 않고 빠른 시간에 정확하게 구현할 줄 아는 능력이 필요합니다.
상황에 따라 dfs로 구현할 수도 있고, next_permutation으로 구현 할 수도 있습니다.
둘 다 알아둔다면 유연하게 사용할 수 있을 것입니다. 설명은 주석을 참고해 주세요.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
|
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
int map[10] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 };
int check[10] = { 0, };
void nCr_with_next_permutation(int n, int r) {
if (r > n) return;
vector<int> mask;
// 1. mask 벡터를 n개만큼 push 합니다.
// 2. 내가 뽑고자 하는 r개에는 0을 push.
// 아닌 경우는 1을 push 합니다.
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (i < r) {
mask.push_back(0);
}
else mask.push_back(1);
}
// 3. mask 벡터를 sort 시킵니다.
// sort는 <algorithm>에 정의되어 있습니다.
sort(mask.begin(), mask.end());
// O(nCr*n)의 시간이 걸립니다.
while (1) {
// 4. n까지 순회하며 mask가 0인 i만 map에서 출력하면 됩니다.
// map 자체는 변하지 않고, mask가 일종의 비트마스크의 마스크같은 개념과 비슷합니다.
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (mask[i] == 0) {
cout << map[i] << ' ';
}
}
cout << '\n';
if(!next_permutation(mask.begin(), mask.end())) break;
}
}
void nPr_with_next_permutation(int n, int r) {
if (r > n) return;
// 1. next_permutation을 적용하게 되면 원본 배열인 map의 순서가 바뀌게 됩니다.
// 따라서 temp 배열에 옮겨 작업을 합니다.
int temp[11];
memcpy(temp, map, sizeof(map));
while (1) {
// 2. nPr은 출력 할 때 뽑고자 하는 r 까지만 출력을 해 주면 됩니다.
for (int i = 0; i < r; i++) {
cout << temp[i] << ' ';
}
cout << '\n';
if (!next_permutation(temp, temp + n)) break;
}
return;
}
void nCr_with_dfs(int n, int r, int now_idx, int depth) {
if (r > n) return;
// 1. dfs를 이용한 조합 구성에서 포인트는
// 파라미터에서 now_idx와 depth를 설정하는 방법입니다.
if (depth == r) {
// 3. r개를 뽑았다면 check 배열 값 중 1로 된 index만 출력합니다.
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (check[i]) cout << map[i] << ' ';
}
cout << '\n';
return;
}
// 2. 두번째 포인트는 시작 인덱스를 now_idx로 잡는 것과
// 다음 dfs에 들어가는 now_idx의 파라미터 값으로 i를 넣는 것입니다.
// nPr_with_dfs와 비교를 하면 쉽게 알 수 있습니다.
for (int i = now_idx; i < n; i++) {
if (check[i]) continue;
check[i] = 1;
nCr_with_dfs(n, r, i, depth + 1);
check[i] = 0;
}
}
void nPr_with_dfs(int n, int r, int depth) {
if (r > n) return;
if (depth == r) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (check[i]) cout << map[i] << ' ';
}
cout << '\n';
return;
}
// nCr과 다르게 시작 인덱스를 0(시작점)으로 설정
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (check[i]) continue;
check[i] = 1;
// nCr과 다르게 인덱스를 설정하는 파라미터가 없음을 알 수 있습니다.
nPr_with_dfs(n, r, depth + 1);
check[i] = 0;
}
}
int main() {
cout << " === nCr_with_next_permutation === " << '\n';
nCr_with_next_permutation(3, 2);
cout << "\n === nPr_with_next_permutation === " << '\n';
nPr_with_next_permutation(3, 2);
cout << "\n === nCr_with_dfs === " << '\n';
nCr_with_dfs(3, 2, 0, 0);
cout << "\n === nPr_with_dfs === " << '\n';
nPr_with_dfs(3, 2, 0);
return 0;
}
http://colorscripter.com/info#e" target="_blank" style="color:#4f4f4ftext-decoration:none">Colored by Color Scripter
|
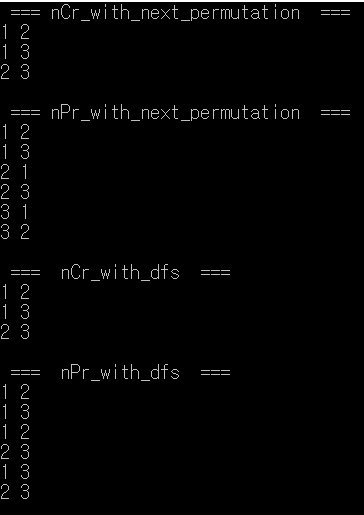
똑같은 nPr 구현이라 해도 next_permutation과 dfs를 사용한 방식의 순서쌍은 순서가 다름을 알 수 있습니다.
이유는 next_permutation의 구현 원리가 dfs와 다르기 때문입니다.
이전글(next_permutation의 내부 구현 방법)을 참조해 주세요.
'알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [BFS] 왜 런타임 에러와 메모리 초과가 발생할까? (0) | 2020.02.17 |
|---|---|
| [C++ STL] next_permutation의 내부 구현 방법 (0) | 2020.02.09 |





